StructForge 1.5.0
dotnet add package StructForge --version 1.5.0
NuGet\Install-Package StructForge -Version 1.5.0
<PackageReference Include="StructForge" Version="1.5.0" />
<PackageVersion Include="StructForge" Version="1.5.0" />
<PackageReference Include="StructForge" />
paket add StructForge --version 1.5.0
#r "nuget: StructForge, 1.5.0"
#:package StructForge@1.5.0
#addin nuget:?package=StructForge&version=1.5.0
#tool nuget:?package=StructForge&version=1.5.0
StructForge
Watch: Benchmarking C# Safe Arrays vs Unsafe Pointers (and why Safe won).
StructForge is a high-performance, zero-allocation data structures library for .NET and Unity.
Designed for performance-critical applications like Game Engines, Real-Time Systems, and High-Frequency Trading, StructForge bridges the gap between standard collections and raw memory manipulation. It focuses on CPU cache locality, hardware intrinsics (SIMD), and minimizing Garbage Collector (GC) pressure.
🚀 Performance Benchmarks
Benchmarks performed on Intel Core i7-13650HX, .NET 8.0.
| Data Structure | Benchmark Scenario | Comparison (vs .NET) | Speedup | Memory |
|---|---|---|---|---|
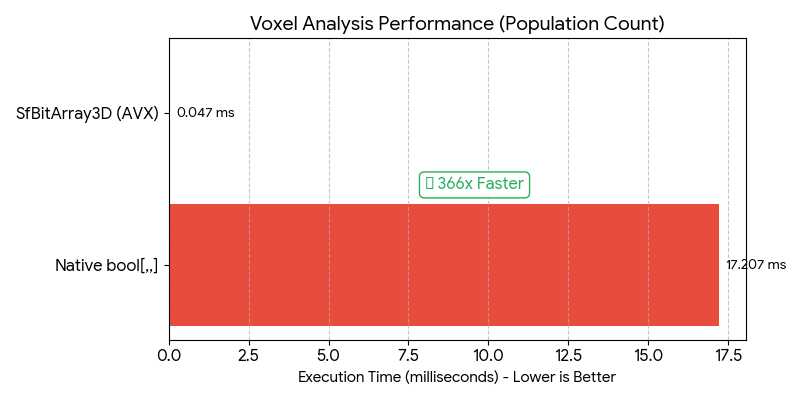
| SfBitArray3D | Voxel Analysis (PopCount) | vs bool[,,] Loop |
🚀 366x Faster | 8x Less RAM |
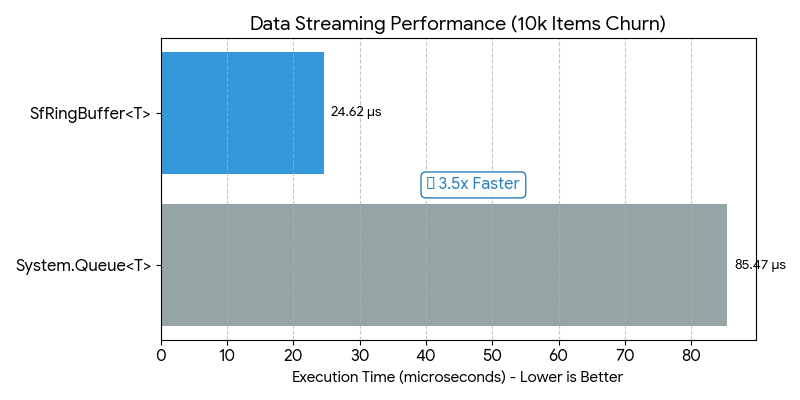
| SfRingBuffer | Data Streaming (Churn) | vs Queue<T> |
🔥 3.5x Faster | Zero Alloc |
| SfBitArray | Logical Masking (AND) | vs bool[] Loop |
⚡ 40x Faster | 8x Less RAM |
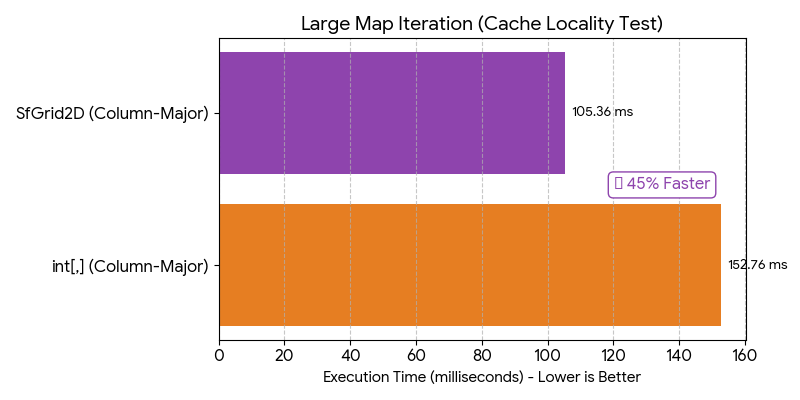
| SfGrid2D | Column-Major Iteration | vs int[,] |
✅ 1.45x Faster | Cache Friendly |
| SfList | Foreach Iteration | vs List<T> |
✅ 1.1x Faster | Zero Alloc |
📊 Performance Visualizations
| Benchmark Scenario | Speedup Analysis |
|---|---|
1. 3D Voxel Analysis<br>(Native bool[,,] vs SfBitArray3D)<br><br>Native arrays struggle with large 3D datasets due to memory overhead. StructForge leverages CPU SIMD instructions (PopCount) to process 64 blocks in parallel. |
 |
2. Data Streaming<br>(System Queue<T> vs SfRingBuffer)<br><br>Standard queues perform array resizing and version checks. SfRingBuffer optimizes throughput by removing modulo arithmetic and utilizing simpler branching logic. |
 |
3. Grid Iteration<br>(Native int[,] vs SfGrid2D)<br><br>Multi-dimensional arrays often cause CPU cache misses during column-major traversal. StructForge's flattened 1D layout ensures linear memory access patterns. |
 |
Detailed benchmark results and methodology can be found in the Benchmarks folder.
✨ Key Features
🚀 What's New in v1.5.0
- SfDictionary is Back: Fully re-architected for zero-allocation performance.
- SfGraph (Core): Added base Graph data structure.
- Debugger Visualizers: Added comprehensive debug views for all collections (Arrays, Graphs, Lists). No more expanding 10 levels to see your data!
⚡ Zero-Allocation Guarantee
All collections in StructForge use custom struct Enumerators.
foreachloops allocate 0 bytes of garbage.- Eliminates GC spikes in hot paths (e.g., Game Loops / Update methods).
- Significantly faster iteration than standard
IEnumerable<T>boxing.
💾 Direct Memory Access (Span Support)
All array-backed structures expose their internal data safely via AsSpan() and AsReadOnlySpan().
- Allows users to perform Zero-Copy operations.
- Enables extremely fast binary serialization using
MemoryMarshal.
🧊 Spatial Optimization
SfGrid2D/SfGrid3D: Uses flattened 1D arrays (z*w*h + y*w + x) to maximize CPU cache hits, unlike .NET's multi-dimensional arrays which can cause cache misses during column-major traversal.SfBitArrayFamily: Bit-packed structures (1D,2D,3D) for boolean maps (Fog of War, Collision), using 8x less memory thanbool[].
🔍 Debugger Friendly
Includes custom DebuggerTypeProxies for all collections.
- View internal items of
SfGraph,SfBitArray,SfDictionaryclearly in the Visual Studio debugger without expanding complex internals.
📦 Installation
Install via NuGet Package Manager:
dotnet add package StructForge
🎮 For Unity Projects
StructForge is fully compatible with Unity 2021.3+ and includes .asmdef files.
Method 1: Install via Git URL (Recommended) You can install directly from Unity Package Manager without extra tools.
Open Unity -> Window -> Package Manager.
Click the "+" button (top-left) -> "Add package from git URL...".
Enter the following URL:
[https://github.com/FurkanKirat/StructForge.git?path=/StructForge](https://github.com/FurkanKirat/StructForge.git?path=/StructForge)
Note: The ?path=/StructForge suffix is required because the package source is located in a subdirectory.
Method 2: Install via OpenUPM If you use openupm-cli, run this command in your project folder:
Bash
openupm add com.kankangames.structforge
Method 3: Manual Installation Download the latest Source Code (zip) from Releases.
Extract the StructForge folder into your Unity project's Packages (or Assets) folder.
📚 Collections Overview
🟢 Linear & Spatial (Zero-Allocation)
SfDictionary<TKey, TValue>: (New in v1.5) High-performance, allocation-free dictionary using open addressing. Faster lookups than native Dictionary with zero GC overhead.
SfGraph<T>: (New in v1.5) Adjacency list-based Graph structure. Efficiently stores nodes and edges. Note: Pathfinding algorithms (A) are scheduled for v1.6.*
SfList<T>: High-performance dynamic array. Supports AsSpan(), RemoveAtSwap (O(1) removal), and direct array access.
SfLinkedList<T>: Doubly linked list implementation. Useful for scenarios requiring frequent insertions/removals from the middle of the collection.
SfEnumSet<TEnum>: Bitmask-based set for Enums. Allocates 2x less memory and performs operations up to 1.7x faster than HashSet.
SfGrid2D<T> / SfGrid3D<T>: Cache-friendly spatial grids. Proven to be up to 45% faster than native arrays in complex iterations.
SfBitArray / SfBitArray2D / SfBitArray3D: SIMD-accelerated bit manipulation structures using hardware intrinsics (POPCNT).
SfRingBuffer<T>: Fixed-size circular buffer. Guaranteed Zero-Allocation on enqueue/dequeue. Ideal for input history, logs, and network packets.
🟡 Trees & Sets (Low-Allocation)
SfAvlTree<T>: A strictly balanced Binary Search Tree. Faster insertions than .NET SortedSet in benchmarks.
SfSortedSet<T>: Backed by SfAvlTree. Provides sorted iteration using a pooled stack buffer (avoiding recursion overhead).
SfBinaryHeap<T>: Array-backed Min-Heap. Can be used as a high-performance Priority Queue.
SfPriorityQueue<TItem, TPriority>: A wrapper around SfBinaryHeap for ease of use with separate priority values.
SfHashSet<T>: Open-addressing hash set with struct enumerators. Optimized for iteration speed.
⚪ Standard Wrappers
SfStack<T> / SfQueue<T>: Optimized implementations using StructForge's underlying array logic for consistent API and performance.
💻 Usage Examples
1. High-Performance Enum Flags (New!)
SfEnumSet uses bitwise operations instead of hashing, making it perfect for RPG stats or inventory flags.
var buffs = new SfEnumSet<Buffs>();
buffs.Add(Buffs.Haste);
buffs.Add(Buffs.Strength);
var debuffs = new SfEnumSet<Buffs>(Buffs.Slow);
// Allocates 272 bytes vs 568 bytes (HashSet)
// Executes ~40% Faster than HashSet.ExceptWith
buffs.ExceptWith(debuffs);
2. Zero-Allocation Game Loop
Iterating over SfList uses a public struct Enumerator, completely avoiding the boxing overhead of IEnumerable<T>.
var entities = new SfList<Entity>(1000);
// ... populate list ...
// 0 GC Allocation here!
foreach (var entity in entities)
{
entity.Update();
}
3. High-Performance Voxel Check
Using SfBitArray3D to check 2 million voxels takes microseconds thanks to CPU Intrinsics.
// Stores 128x128x128 world (2M blocks) in ~256 KB RAM (vs 2MB for bool[])
var voxels = new SfBitArray3D(128, 128, 128);
voxels.SetUnchecked(10, 50, 10, true);
// Hardware Accelerated PopCount (~360x Faster than loop)
int activeBlocks = voxels.CountTrue();
4. Zero-Copy Binary Serialization
Since SfGrid stores data contiguously, you can cast it to bytes and write to disk instantly without intermediate buffers.
public void SaveTerrain(SfGrid2D<int> terrain, Stream stream)
{
// 1. Get data as Span (No Copy)
ReadOnlySpan<int> data = terrain.AsReadOnlySpan();
// 2. Reinterpret as Bytes (User-side optimization)
var bytes = System.Runtime.InteropServices.MemoryMarshal.AsBytes(data);
// 3. Write to disk instantly
stream.Write(bytes);
}
5. Ring Buffer for Logs
Ideal for scenarios where you need to keep the last N items without generating garbage.
var logs = new SfRingBuffer<string>(100); // Fixed capacity
// When full, it automatically overwrites the oldest item.
// No resizing, No memory allocation.
logs.Enqueue("Player joined");
logs.Enqueue("Game started");
foreach (var log in logs)
{
Console.WriteLine(log);
}
⚠️ Important Notes
- Thread Safety
StructForge collections are not thread-safe by default.
This is a design choice to ensure maximum single-threaded performance (avoiding locking overhead).
Use external synchronization when accessing from multiple threads.
📄 License
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for more information.
| Product | Versions Compatible and additional computed target framework versions. |
|---|---|
| .NET | net5.0 was computed. net5.0-windows was computed. net6.0 was computed. net6.0-android was computed. net6.0-ios was computed. net6.0-maccatalyst was computed. net6.0-macos was computed. net6.0-tvos was computed. net6.0-windows was computed. net7.0 was computed. net7.0-android was computed. net7.0-ios was computed. net7.0-maccatalyst was computed. net7.0-macos was computed. net7.0-tvos was computed. net7.0-windows was computed. net8.0 was computed. net8.0-android was computed. net8.0-browser was computed. net8.0-ios was computed. net8.0-maccatalyst was computed. net8.0-macos was computed. net8.0-tvos was computed. net8.0-windows was computed. net9.0 was computed. net9.0-android was computed. net9.0-browser was computed. net9.0-ios was computed. net9.0-maccatalyst was computed. net9.0-macos was computed. net9.0-tvos was computed. net9.0-windows was computed. net10.0 was computed. net10.0-android was computed. net10.0-browser was computed. net10.0-ios was computed. net10.0-maccatalyst was computed. net10.0-macos was computed. net10.0-tvos was computed. net10.0-windows was computed. |
| .NET Core | netcoreapp3.0 was computed. netcoreapp3.1 was computed. |
| .NET Standard | netstandard2.1 is compatible. |
| MonoAndroid | monoandroid was computed. |
| MonoMac | monomac was computed. |
| MonoTouch | monotouch was computed. |
| Tizen | tizen60 was computed. |
| Xamarin.iOS | xamarinios was computed. |
| Xamarin.Mac | xamarinmac was computed. |
| Xamarin.TVOS | xamarintvos was computed. |
| Xamarin.WatchOS | xamarinwatchos was computed. |
-
.NETStandard 2.1
- System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe (>= 6.1.2)
NuGet packages
This package is not used by any NuGet packages.
GitHub repositories
This package is not used by any popular GitHub repositories.
v1.5.0 Release Notes
🔥 New: SfDictionary: Added high-performance, allocation-free dictionary implementation.
🕸️ New: SfGraph (Core): Introduced the base Graph data structure architecture (Adjacency List).
Note: Pathfinding algorithms (A*, BFS, DFS) are scheduled for the upcoming v1.6.0 release.
🛠️ Debugging: Added comprehensive DebuggerTypeProxies (Visualizers) for all collections. You can now view internal items of SfGraph, SfBitArray, and others directly in Visual Studio debugger.
✨ Improvements: General stability improvements and optimizations.
```


